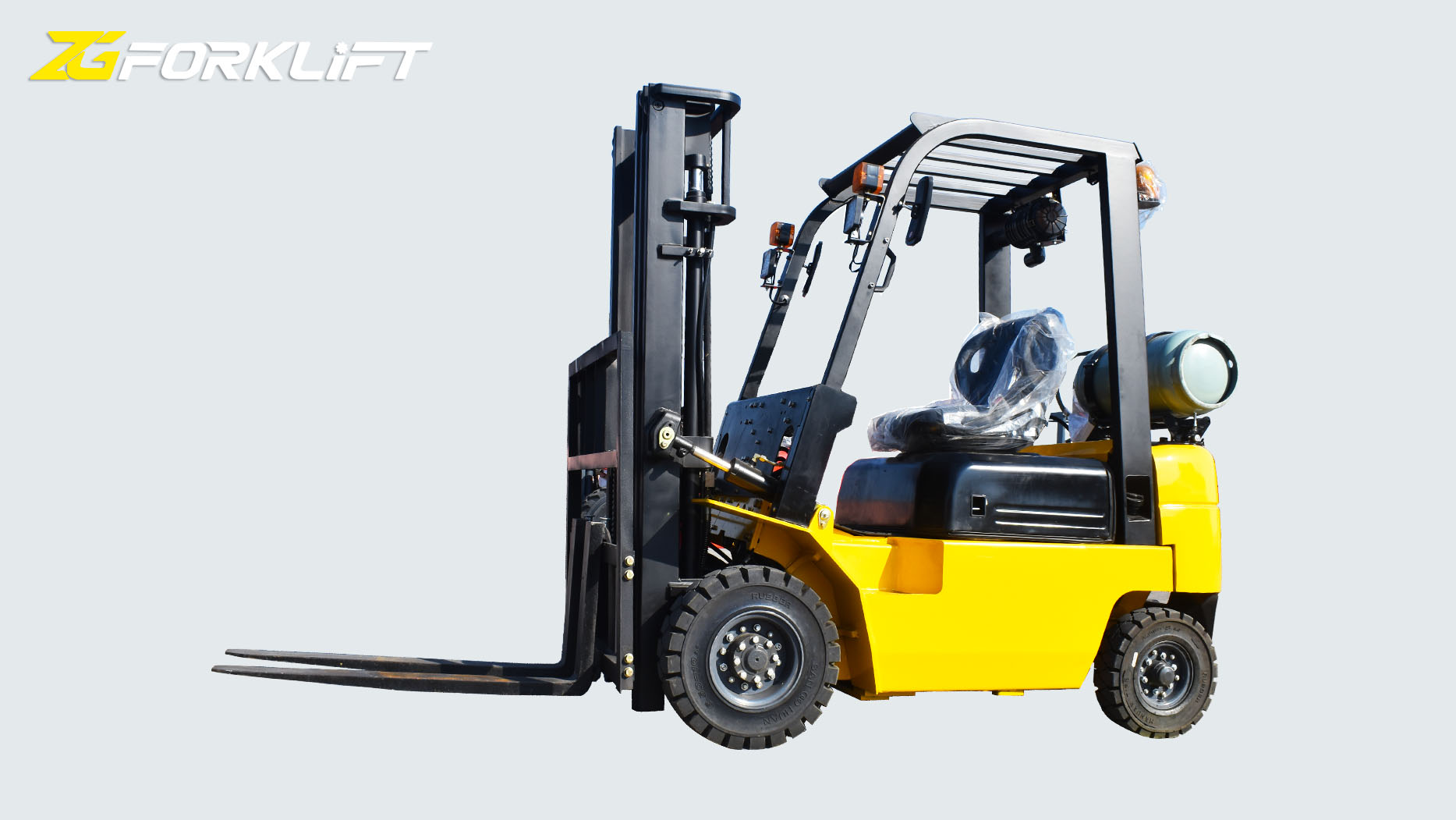
Propane-powered forklifts are a popular choice in many industries due to their performance and cost-effectiveness. However, understanding the nature of the fumes emitted by these vehicles is crucial for ensuring workplace safety and environmental compliance.
Primary Emissions:
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): The primary byproduct of propane combustion is carbon dioxide. CO2 is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Water Vapor (H2O): Water vapor is also a significant product of propane combustion.
Minor Emissions:
Carbon Monoxide (CO): Incomplete combustion of propane can produce carbon monoxide (CO). CO is an odorless, colorless, and highly toxic gas that can cause serious health problems, including headache, dizziness, nausea, and even death in high concentrations.
Hydrocarbons (HC): Unburned or partially burned hydrocarbons, such as methane and propane, can be emitted. These contribute to air pollution and smog formation.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): In certain operating conditions, small amounts of nitrogen oxides (NOx), such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), may be produced. NOx contributes to smog and acid rain.
Particulate Matter (PM): While generally lower than diesel emissions, some particulate matter, including soot and ash, can be emitted from propane engines.
Factors Affecting Emissions:
Engine Maintenance: Proper engine maintenance, including regular tune-ups and filter replacements, is crucial for minimizing emissions.
Engine Load: The engine load significantly impacts emissions. Higher loads generally result in higher emissions.
Air-Fuel Ratio: The air-fuel mixture in the engine plays a critical role in determining emission levels. An improperly adjusted air-fuel ratio can lead to increased emissions of CO and HC.
Engine Operating Conditions: Factors such as engine speed, operating temperature, and altitude can also influence emission levels.
Fuel Quality: The quality of the propane fuel used can affect emissions. Using high-quality propane can help minimize emissions.
Environmental and Health Concerns:
Air Pollution: Emissions from propane forklifts contribute to air pollution, which can have adverse effects on human health and the environment.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: CO2 emissions from propane combustion contribute to climate change.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Exposure to high levels of CO can be fatal. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent CO buildup in enclosed spaces.
Mitigating Emissions:
Proper Maintenance: Regular engine maintenance, including tune-ups, filter replacements, and proper fuel system maintenance, is crucial for minimizing emissions.
Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in indoor environments to prevent the buildup of CO and other emissions.
Emission Control Technologies: Explore the use of advanced emission control technologies, such as catalytic converters, to reduce emissions.
Alternative Fuels: Consider alternative fuels, such as propane-methane blends or renewable propane, to reduce environmental impact.
Operator Training: Train operators on proper driving techniques, including minimizing idling time and avoiding rapid acceleration and deceleration, to reduce emissions.
Conclusion:
Propane-powered forklifts offer several advantages, but it's important to understand the potential environmental and health impacts of their emissions. By implementing proper maintenance practices, utilizing advanced emission control technologies, and ensuring adequate ventilation, businesses can minimize the environmental impact of their propane-powered equipment while maintaining a safe and productive work environment.
Post time:Feb.12.2025